These animated lower body plyometric exercises can be used to develop power in any sport that involves sprinting, jumping, quick changes of direction and kicking etc. They are most effective when completed in conjunction with a suitable strength training program or following a phase of maximal strength training...
For more details on how to develop a sport-specific strength and power program, and where plyometrics fits into the overall plan, see the sport specific approach to strength training programs.
There is no evidence to suggest the risk of injury is increased during plyometric training in adults. However, as a precaution several safety guidelines have been recommended to keep plyometric exercises as safe as possible. Because plyometrics has received little scientific study compared to conventional strength training, there are no definitive guidelines regarding sets, repetitions and frequency etc. The National Strength & Conditioning Association and several leading experts in the field have proposed parameters that will help coaches and athletes design an effective training plan.
For details on how to put together a safe and effective plyometric training program click here.
Plyometric Exercise Intensity
Not all plyometric exercises are equal in intensity. Skipping exercises for example, are relatively light while single leg bounds and depth jumps are the most intense. A program should progress gradually from lower intensity drills to more advanced plyometric exercises particularly in an individual with less strength training experience.
The number of plyometric exercises is typically kept to a minimum also. A typical session may contain only two or three lower body plyometric exercises interspersed with upper body plyometric drills if theyre appropriate for that sport.
Correct exercise selection is essential! While there are many plyometric exercises below only a few will be suitable for any one particular sport or event. Again, for all the details on exercise selection, sets, repetitions, rest intervals and so on, see this plyometric training article.
Lower Body Plyometric Exercises (Low Intensity)
 Squat Jumps
Squat Jumps1. Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, trunk flexed forward slightly with back straight in a neutral position.
2. Arms should be in the ready" position with elbows flexed at approximately 90.
3. Lower body where thighs are parallel to ground and immediately explode upwards vertically and drive arms up. Do not hold a squat position before jumping up keep the time between dipping down and jumping up to a minimum.
4. Land on both feet. Rest for 1-2 seconds and repeat
Prior to takeoff extend the ankles to their maximum range (full plantar flexion) to ensure proper mechanics.
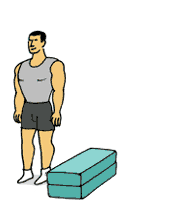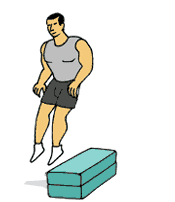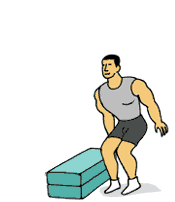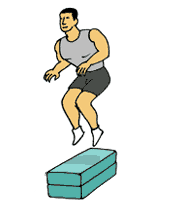
 Jump to Box
Jump to Box1.Stand facing box with feet slightly wider than hip-width apart.
2.Lower body into a semi-squat position and immediately jump up onto box. Do not hold a squat position before jumping up keep the time between dipping down and jumping up to a minimum.
3. Feet should land softly on box. Step back down (not jump back down) and repeat.
 Lateral Jump to Box
Lateral Jump to Box1. Stand side on to box with feet slightly wider than hip-width apart.
2. Lower body into a semi-squat position and jump up onto box. Do not hold a squat position before jumping up keep the time between dipping down and jumping up to a minimum.
3. Feet should land softly on box. Step back down (not jump back down) and repeat.
Lower Body Plyometric Exercises (Moderate Intensity)
 Split Squat Jumps
Split Squat Jumps1. Stand with feet hip width apart. Take left leg and step back approximately 2 feet standing on the ball of back foot.
2. Feet should be positioned at a staggered stance with head and back erect and straight in a neutral position.
3. Lower body by bending at right hip and knee until thigh is parallel to floor then immediately explode vertically.
4. Switch feet in the air so that the back foot lands forward and vice versa.
Prior to takeoff extend the ankles to their maximum range (full plantar flexion) ensure proper mechanics.
 Tuck Jumps
Tuck Jumps1. Stand with feet shoulder-width apart, knees slightly bent, with arms at sides.
2. Jump up bringing knees up to chest.
3. Land on balls of feet and repeat immediately.
4. Remember to reduce ground contact time by landing soft on feet and springing into air.
 Lateral Box Push Offs
Lateral Box Push Offs1. Stand to side of box and place the left foot on top of box.
2. Push off the box using the left leg only and explode vertically as high as possible. Drive the arms forward and up for maximum height.
3. Land with right foot on the box and left foot on the ground to the other side of the box.
4. Repeat from this side.
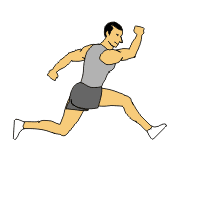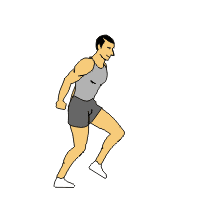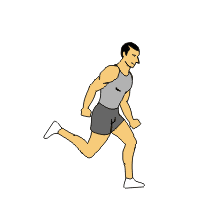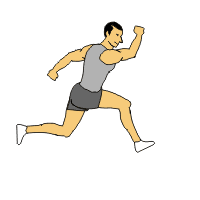 Bounding
Bounding1. Jog into the start of the drill for forward momentum.
2. After a few feet, forcefully push off with the left foot and bring the leg forward. At same time drive your right arm forward.
3. Repeat with other leg and arm
4. This exercise is an exaggerated running motion focusing on foot push-off and air time.
 Bounding with Rings
Bounding with Rings1. Jog into the start of the drill for forward momentum.
2. After a few feet, forcefully push off with the left foot and bring the right leg forward. At same time swing left arm forward and land into the first ring, which is 3-4 feet out and to the left, with the right foot.
3. Continue and repeat with other leg and arm into the second ring, which is now 3-4 feet up and to the right.
4. This exercise is an exaggerated running motion focusing on foot push-off and air time.
 Box Drill with Rings
Box Drill with Rings1. Stand with feet slightly wider than hip-width apart with your body facing the first ring.
2. Hop forward using both feet and land in first ring.
3. Now hop to the left and land in the ring to the side. Now jump backwards to land in ring behind you. Finish by jumping to your right to land in final ring.
4. Rest and repeat. Remember to keep ground contact time between bounds to a minimum.Hurdle Jumps
 Lateral Hurdle Jumps
Lateral Hurdle Jumps1. Stand beside object to be cleared.
2. Bring knees up and jump vertically but also laterally off ground and over the barrier.
3. Land on both feet and immediately jump the other direction over barrier.
4. Try not to pause between jumps or sink down into a squat position.
Lower Body Plyometric Exercises (High Intensity)
 Zigzag Hops
Zigzag Hops1. Stand to the left of an agility ladder or similar object approximately 1-2 feet away.
2. Forcefully push off both feet and land the on the other side of the ladder.
3. Repeat and land feet back on the other side, continue repeating and so on down the ladder.4. Do not "double hop" upon each landing and keep ground contact time to a minimum.
Single Leg Tuck Jump
This is the same as the tuck jump exercise above only one leg is used. Upon landing another jump is performed immediately with minimal ground contact time and with the same leg for the desired number of repetitions. This is repeated for the other leg after a rest period. Single leg plyometric exercises are typically more advanced and require greater strength and balance. They are suitable for sports were a takeoff is completed on one leg.
 Single Leg Lateral Hops
Single Leg Lateral Hops1. Start by standing on one leg with your hands on your waist or at your sides.
2. Proceed to hop to the side while maintaining your balance and hop back to the starting position.
3. You can place a rope on the ground or any object on the ground. The object can be small in size and height or large to increase difficulty.
4. Repeat continuously.
 Depth Jumps
Depth Jumps1. Stand on box with toes close to edge, feet shoulder width apart.
2. Step off (do not jump off) box and land on both feet. Immediately jump up as high as possible and reach up with both hands towards. The jump should be vertical with no horizontal movement.
4. Ground contact time should be short unlike in the diagram. Landing should be soft.Note: Start with a box height of 30cm (12in). Intensity can be increased by gradually increasing the box height to a maximum of 107cm (42in) but this is only for experienced athletes with a substantial strength training background.
Please look out for more sample plyometrics exercises in the main plyometrics section.
